Smart Food Safe participating in SQF Unites 2025, from March 2nd - 5th, 2025 at the Hyatt Regency, Orlando, Florida. Meet us at Booth #16 .
Smart Food Safe participating in SQF Unites 2025, from March 2nd - 5th, 2025 at the Hyatt Regency, Orlando, Florida. Meet us at Booth #16 .
Smart Food Safe participating in SQF Unites 2025, from March 2nd - 5th, 2025 at the Hyatt Regency, Orlando, Florida. Meet us at Booth #16 .
Smart Food Safe participating in SQF Unites 2025, from March 2nd - 5th, 2025
at the Hyatt Regency, Orlando, Florida. Meet us at Booth #16 .


Smart Food Safe participating in
Petfood Forum 2025, from April 28th to 30th in Kansas City, Missouri. Meet us at Booth #910.
Document Management
Complying With Quality Management System Documentation Requirements
Complying With Quality Management System Documentation Requirements
Arundhathy Shabu
April 4, 2024

Document Management
Complying With Quality Management System Documentation Requirements
Arundhathy Shabu
April 4, 2024
Complying With Quality Management System Documentation Requirements
Document Management

Arundhathy Shabu
.
April 4, 2024
The two key concepts that define the success of an enterprise are its capability to maintain safety and quality in all operations. Safety revolves around ensuring people and the environment are protected from harm, whereas quality is about the extent to which products or services meet or exceed customer expectations by staying in compliance with the established quality control processes and standards.
A Quality Management System (QMS) elaborates on specific documentation requirements essential for industries to deliver a product or service that is fit for its intended purpose and represents the highest level of quality for customer satisfaction and upholding brand reputation. Employing techniques that make document compliance a park in the walk to adhere to quality management documentation requirements can be enhanced by implementing an integrated quality document management system. Let’s delve into the workings of such a system, the key considerations for its adoption, and the prominent benefits it highlights.
Breaking Down Quality Management System (QMS) Documentation
A QMS can be described as a structured framework that records processes, protocols, and assigned roles aimed at attaining quality policies and goals. It serves to orchestrate and guide an organization’s endeavors in aligning with customer expectations and regulatory standards while improving its ongoing performance and productivity. Documentation serves as the cornerstone of QMS, establishing a robust framework for an organization’s operations and processes. A well-structured QMS documentation hierarchy accommodates the following levels:
1. Policy
Quality policies outline the organization’s overarching principles and commitments regarding quality management. These policies establish the organization’s quality objectives and guide on how quality should be managed throughout the organization. Quality policies are typically concise statements endorsed by top management and communicated to all relevant stakeholders.
2. Manual
The quality manual provides an overview of the organization’s QMS, including its scope, objectives, processes, and interaction between various elements of the system. The quality manual serves as a reference point for understanding the organization’s approach to quality management.
3. Procedures
Quality procedures define the detailed steps and activities required to perform specific processes within the QMS. These procedures typically include instructions on how to carry out tasks related to quality management, such as document control, corrective and preventive actions, internal audits, and management reviews.
4. Work Instructions
Work Instructions provide step-by-step guidance on how to perform specific tasks or activities within a process. Unlike procedures, which describe the overall process, work instructions offer detailed instructions, including methods, tools, and resources required to complete a task effectively and consistently. Work instructions are often used for tasks that require precision or adherence to specific standards.
5. Forms and Records
Forms and Records are documents used to capture and record information related to quality management activities. Forms may include templates for recording data, such as inspection reports, non-conformance reports, and training records. Records, on the other hand, document evidence of compliance with quality management requirements, such as audit reports, calibration records, and customer feedback.
The QMS documentation structure should be designed to be clear, accessible, and scalable to accommodate changes and updates over time. It should also be aligned with the organization’s goals, objectives, and industry-specific requirements to ensure the effectiveness and efficiency of the quality management processes. Regular review and maintenance of the documentation hierarchy are indispensable aspects of an organization’s QMS.
Food Safety Management Software
Boost your food business’s hygiene standards with Smart Food Safe’s tech-driven solutions—streamline 4C processes to yield optimal results, and ensure compliance effortlessly.

Food Safety Management Software
Boost your food business’s hygiene standards with Smart Food Safe’s tech-driven solutions—streamline 4C processes to yield optimal results, and ensure compliance effortlessly.
General QMS Documentation Requirements According to ISO 9001 & ISO 10013:2021
ISO 9001 stands as the globally recognized standard outlining the prerequisites for establishing a QMS. As the cornerstone of the ISO 9000 series, ISO 9001 stands as the sole standard within this series eligible for organizational certification. It serves as the basic resource for organizations to develop their QMS. ISO 10013:2021 is a technical report offering guidance on creating and maintaining quality manuals, detailing the structure and content of such documents for effective QMS documentation, and aiding organizations in implementing quality management practices.
The necessary level of documentation in a QMS is determined by the scale and extent of the organization. Below are the foundational documents needed in a QMS, as per ISO 9001 and recommended by 10013:2001:
⇒ Quality Policy and Quality Manual
The quality policy outlines the principles and objectives aligned with an organization’s mission, while the quality manual serves as a top-level guide demonstrating how the QMS functions, including scope, policies, procedures, regulations, and reference to documents or records, to furnish clear communication and adherence to quality standards.
⇒ Quality Control Procedures
Quality control procedures document the processes governing quality control within an establishment, narrating the methods necessary to maintain product/service quality. This documentation is vital for establishing clear quality assessment criteria, bringing consistency, compliance with standards, and meeting quality certification requirements.
⇒ Key Processes and Workflows
Identifying and documenting key processes of an organization is critical for ensuring continuous quality products/services by thoroughly explaining all activities necessary for delivering value to customers. This documentation involves listing key processes, detailing workflows including steps, roles, inputs/outputs, resources, presenting them through diagrams, and specifying key performance indicators (KPIs).
⇒ Records and Compliance Documents
Compliance records show evidence that the organization has performed the imperative quality activities and adheres to the established procedures. Maintaining compliance records is important for reflecting adherence to quality standards, and regulatory requirements, and supporting audits and improvement efforts within the organization. These records encompass training records, non-conformance reports, audit reports, equipment maintenance records, and regulatory compliance reports, all of which depict the organization’s commitment to quality measures and compliance.
⇒ Change and Version Control
Change and version control help in tracking and managing modifications in processes or products/services over time, ensuring QMS effectiveness. This involves a systematic process including steps such as change request, impact analysis, approval, implementation, and review/reporting, alongside maintaining an up-to-date version log.
⇒ Internal and External Audits
Internal and external audits are needed for assessing the effectiveness of a QMS, necessitating extensive documentation including audit schedules, scopes, objectives, and detailed audit plans with criteria and responsibilities. Following each audit, reports detailing findings, methodology, observations, and recommendations should be generated by auditors to facilitate improvements within the QMS.
⇒ Non-Conformities and Corrective Actions
Non-conformities, which signify failures to meet requirements or standards, must be documented with information such as the nature, root cause, and personnel involved. This documentation aids in the effective resolution of issues and necessitates documenting corrective and preventive actions to address loopholes, improve processes, and demonstrate commitment to quality control.
⇒ Risk and Opportunity Management
Effective management of risks and opportunities is integral to quality control within any organization, demanding documentation with lists detailing identified risks and opportunities, along with associated strategies and evaluation criteria, ascertaining strategic risk management.
⇒ Staff Training and Competency
Staff training and competency enable employees to perform their roles effectively and understand organizational procedures, directly impacting quality outcomes. Documentation of training plans, records of past employee training, and assessments of employee competencies allow employees to be equipped to fulfill their responsibilities through appropriate documentation strategies.
⇒ Quality Plans and Objectives
The quality plan outlines procedures, processes, and resources necessary to achieve specific quality objectives, ranging from enhancing employee competency to reducing product performance complaints. Clear quality objectives are defined first, followed by the development of a comprehensive plan detailing scope, roles/responsibilities, action steps, resources, and timeframe to ensure effective execution.
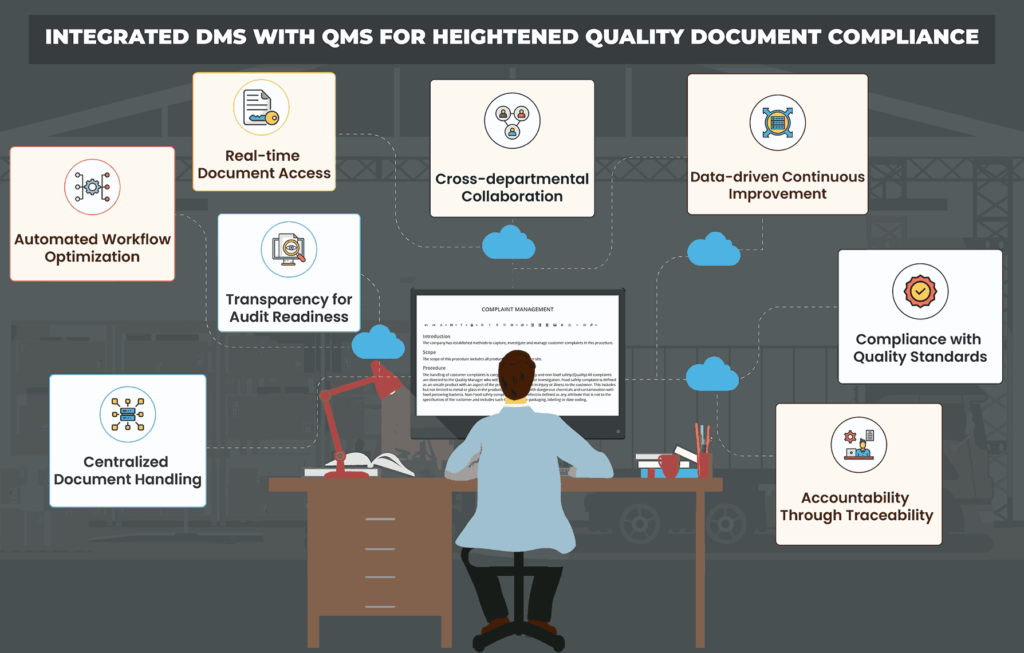
Overcoming Challenges in Quality Document Compliance Management with an Integrated DMS-QMS
Many organizations still rely on manual processes or paper-based systems for managing quality documents. Such systems are prone to errors, and inefficiencies, and are not scalable, making it difficult to keep up with evolving compliance requirements. Integrating a document management system with a quality management system offers numerous benefits, including improved document control, enhanced collaboration, streamlined compliance, and increased operational efficiency.
1. Document Proliferation
Organizations deal with numerous documents related to quality management, including policies, procedures, work instructions, specifications, and regulatory standards.
Managing a large volume of documents becomes challenging, leading to difficulties in version control, document retrieval, and ensuring the accuracy of information.
How an Integrated DMS-QMS can help?
An integrated DMS-QMS provides centralized storage and organization, reducing duplication and ensuring a single source of truth for documents, mitigating proliferation issues.
2. Version Control Issues
Without a centralized system for document management, tracking document versions becomes complex.
Multiple versions of documents may exist simultaneously, leading to confusion among users about which version is the latest and most accurate.
How an Integrated DMS-QMS can help?
Through automated versioning and tracking within the integrated DMS-QMS, teams can easily manage document revisions, ensuring that the latest version is always accessible and eliminating version control discrepancies.
3. Access Control and Security
Ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive quality documents is crucial for compliance and data security.
Without proper access controls, there’s a risk of unauthorized access, manipulation, or loss of critical documents.
How an Integrated DMS-QMS can help?
Implementing role-based access controls and encryption protocols within the integrated DMS-QMS enhances document security, limiting access to authorized personnel and safeguarding sensitive information.
4. Cross-Functional Collaboration
Quality documents often require input and approval from multiple stakeholders across different departments.
Coordinating document review and approval processes among various stakeholders can be challenging, leading to delays and communication gaps.
How an Integrated DMS-QMS can help?
The integrated DMS-QMS facilitates seamless collaboration among different departments and teams by providing real-time document sharing, commenting, and editing capabilities, fostering cross-functional communication and efficiency.
5. Regulatory Compliance
Industries are subject to stringent regulatory requirements and standards governing quality management practices.
Ensuring that quality documents comply with these regulations requires continuous monitoring and updates, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
How an Integrated DMS-QMS can help?
By incorporating regulatory requirements directly into document templates and workflows, the integrated DMS-QMS ensures compliance at every stage, streamlining regulatory adherence and reducing the risk of non-compliance.
6. Audit Readiness
Organizations must be prepared for audits by regulatory bodies or external certifying agencies.
Gathering and presenting the necessary documentation during audits can be daunting, especially if documents are scattered across disparate systems or are not well-organized.
How an Integrated DMS-QMS can help?
With document tracking, audit trails, and customizable reporting features, the integrated DMS-QMS prepares organizations for audits by providing easy access to documented processes, revisions, and compliance records.
7. Document Retention and Archiving
Compliance standards often dictate specific requirements for document retention and archiving.
Managing the lifecycle of documents, including retention periods and disposal procedures, poses challenges without a structured approach to document management.
How an Integrated DMS-QMS can help?
Automated retention policies and archival features within the integrated DMS-QMS ensure that documents are stored, managed, and disposed of in accordance with regulatory requirements and organizational policies, simplifying retention and archiving processes.
By linking these systems, organizations can establish and manage quality documentation, mitigate compliance risks, and drive continuous improvement initiatives in the most optimized manner. Embracing this integration is the need of the hour for organizations striving to maintain competitiveness, uphold regulatory standards, and achieve excellence in quality management practices.
Smart Food Safe’s One-Stop Solution for QMS Document Compliance
As a prominent provider of software solutions, Smart Food Safe features Smart Docs as an end-to-end digital tool to maintain document compliance within the quality management system in enterprises.
Our integrated quality document management system offers easy access to standard templates and facilitates migration to the latest versions, enhancing your document control experience. With streamlined document creation, editing, and organization through an intuitive interface and seamless cloud storage integration, Smart Docs simplifies your workflow. Centralized document management, customizable folder structures, and advanced search filters ensure easy retrieval of critical documents. Task scheduling, automated workflows, traceable audit trails, and smart linking capabilities further enhance productivity, accountability, and regulatory compliance.

Quality and Food Safety Management Software
Food Safety and Quality Management Software to streamline processes, track compliance, ensure traceability and maintain audit readiness with global quality and food safety standards
The two key concepts that define the success of an enterprise are its capability to maintain safety and quality in all operations. Safety revolves around ensuring people and the environment are protected from harm, whereas quality is about the extent to which products or services meet or exceed customer expectations by staying in compliance with the established quality control processes and standards.
A Quality Management System (QMS) elaborates on specific documentation requirements essential for industries to deliver a product or service that is fit for its intended purpose and represents the highest level of quality for customer satisfaction and upholding brand reputation. Employing techniques that make document compliance a park in the walk to adhere to quality management documentation requirements can be enhanced by implementing an integrated quality document management system. Let’s delve into the workings of such a system, the key considerations for its adoption, and the prominent benefits it highlights.
Breaking Down Quality Management System (QMS) Documentation
A QMS can be described as a structured framework that records processes, protocols, and assigned roles aimed at attaining quality policies and goals. It serves to orchestrate and guide an organization’s endeavors in aligning with customer expectations and regulatory standards while improving its ongoing performance and productivity. Documentation serves as the cornerstone of QMS, establishing a robust framework for an organization’s operations and processes. A well-structured QMS documentation hierarchy accommodates the following levels:
1. Policy
Quality policies outline the organization’s overarching principles and commitments regarding quality management. These policies establish the organization’s quality objectives and guide on how quality should be managed throughout the organization. Quality policies are typically concise statements endorsed by top management and communicated to all relevant stakeholders.
2. Manual
The quality manual provides an overview of the organization’s QMS, including its scope, objectives, processes, and interaction between various elements of the system. The quality manual serves as a reference point for understanding the organization’s approach to quality management.
3. Procedures
Quality procedures define the detailed steps and activities required to perform specific processes within the QMS. These procedures typically include instructions on how to carry out tasks related to quality management, such as document control, corrective and preventive actions, internal audits, and management reviews.
4. Work Instructions
Work Instructions provide step-by-step guidance on how to perform specific tasks or activities within a process. Unlike procedures, which describe the overall process, work instructions offer detailed instructions, including methods, tools, and resources required to complete a task effectively and consistently. Work instructions are often used for tasks that require precision or adherence to specific standards.
5. Forms and Records
Forms and Records are documents used to capture and record information related to quality management activities. Forms may include templates for recording data, such as inspection reports, non-conformance reports, and training records. Records, on the other hand, document evidence of compliance with quality management requirements, such as audit reports, calibration records, and customer feedback.
The QMS documentation structure should be designed to be clear, accessible, and scalable to accommodate changes and updates over time. It should also be aligned with the organization’s goals, objectives, and industry-specific requirements to ensure the effectiveness and efficiency of the quality management processes. Regular review and maintenance of the documentation hierarchy are indispensable aspects of an organization’s QMS.
Food Safety Management Software
Boost your food business’s hygiene standards with Smart Food Safe’s tech-driven solutions—streamline 4C processes to yield optimal results, and ensure compliance effortlessly.

General QMS Documentation Requirements According to ISO 9001 & ISO 10013:2021
ISO 9001 stands as the globally recognized standard outlining the prerequisites for establishing a QMS. As the cornerstone of the ISO 9000 series, ISO 9001 stands as the sole standard within this series eligible for organizational certification. It serves as the basic resource for organizations to develop their QMS. ISO 10013:2021 is a technical report offering guidance on creating and maintaining quality manuals, detailing the structure and content of such documents for effective QMS documentation, and aiding organizations in implementing quality management practices.
The necessary level of documentation in a QMS is determined by the scale and extent of the organization. Below are the foundational documents needed in a QMS, as per ISO 9001 and recommended by 10013:2001:
⇒ Quality Policy and Quality Manual
The quality policy outlines the principles and objectives aligned with an organization’s mission, while the quality manual serves as a top-level guide demonstrating how the QMS functions, including scope, policies, procedures, regulations, and reference to documents or records, to furnish clear communication and adherence to quality standards.
⇒ Quality Control Procedures
Quality control procedures document the processes governing quality control within an establishment, narrating the methods necessary to maintain product/service quality. This documentation is vital for establishing clear quality assessment criteria, bringing consistency, compliance with standards, and meeting quality certification requirements.
⇒ Key Processes and Workflows
Identifying and documenting key processes of an organization is critical for ensuring continuous quality products/services by thoroughly explaining all activities necessary for delivering value to customers. This documentation involves listing key processes, detailing workflows including steps, roles, inputs/outputs, resources, presenting them through diagrams, and specifying key performance indicators (KPIs).
⇒ Records and Compliance Documents
Compliance records show evidence that the organization has performed the imperative quality activities and adheres to the established procedures. Maintaining compliance records is important for reflecting adherence to quality standards, and regulatory requirements, and supporting audits and improvement efforts within the organization. These records encompass training records, non-conformance reports, audit reports, equipment maintenance records, and regulatory compliance reports, all of which depict the organization’s commitment to quality measures and compliance.
⇒ Change and Version Control
Change and version control help in tracking and managing modifications in processes or products/services over time, ensuring QMS effectiveness. This involves a systematic process including steps such as change request, impact analysis, approval, implementation, and review/reporting, alongside maintaining an up-to-date version log.
⇒ Internal and External Audits
Internal and external audits are needed for assessing the effectiveness of a QMS, necessitating extensive documentation including audit schedules, scopes, objectives, and detailed audit plans with criteria and responsibilities. Following each audit, reports detailing findings, methodology, observations, and recommendations should be generated by auditors to facilitate improvements within the QMS.
⇒ Non-Conformities and Corrective Actions
Non-conformities, which signify failures to meet requirements or standards, must be documented with information such as the nature, root cause, and personnel involved. This documentation aids in the effective resolution of issues and necessitates documenting corrective and preventive actions to address loopholes, improve processes, and demonstrate commitment to quality control.
⇒ Risk and Opportunity Management
Effective management of risks and opportunities is integral to quality control within any organization, demanding documentation with lists detailing identified risks and opportunities, along with associated strategies and evaluation criteria, ascertaining strategic risk management.
⇒ Staff Training and Competency
Staff training and competency enable employees to perform their roles effectively and understand organizational procedures, directly impacting quality outcomes. Documentation of training plans, records of past employee training, and assessments of employee competencies allow employees to be equipped to fulfill their responsibilities through appropriate documentation strategies.
⇒ Quality Plans and Objectives
The quality plan outlines procedures, processes, and resources necessary to achieve specific quality objectives, ranging from enhancing employee competency to reducing product performance complaints. Clear quality objectives are defined first, followed by the development of a comprehensive plan detailing scope, roles/responsibilities, action steps, resources, and timeframe to ensure effective execution.
Overcoming Challenges in Quality Document Compliance Management with an Integrated DMS-QMS
Many organizations still rely on manual processes or paper-based systems for managing quality documents. Such systems are prone to errors, and inefficiencies, and are not scalable, making it difficult to keep up with evolving compliance requirements. Integrating a document management system with a quality management system offers numerous benefits, including improved document control, enhanced collaboration, streamlined compliance, and increased operational efficiency.
1. Document Proliferation
Organizations deal with numerous documents related to quality management, including policies, procedures, work instructions, specifications, and regulatory standards.
Managing a large volume of documents becomes challenging, leading to difficulties in version control, document retrieval, and ensuring the accuracy of information.
How an Integrated DMS-QMS can help?
An integrated DMS-QMS provides centralized storage and organization, reducing duplication and ensuring a single source of truth for documents, mitigating proliferation issues.
2. Version Control Issues
Without a centralized system for document management, tracking document versions becomes complex.
Multiple versions of documents may exist simultaneously, leading to confusion among users about which version is the latest and most accurate.
How an Integrated DMS-QMS can help?
Through automated versioning and tracking within the integrated DMS-QMS, teams can easily manage document revisions, ensuring that the latest version is always accessible and eliminating version control discrepancies.
3. Access Control and Security
Ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive quality documents is crucial for compliance and data security.
Without proper access controls, there’s a risk of unauthorized access, manipulation, or loss of critical documents.
How an Integrated DMS-QMS can help?
Implementing role-based access controls and encryption protocols within the integrated DMS-QMS enhances document security, limiting access to authorized personnel and safeguarding sensitive information.
4. Cross-Functional Collaboration
Quality documents often require input and approval from multiple stakeholders across different departments.
Coordinating document review and approval processes among various stakeholders can be challenging, leading to delays and communication gaps.
How an Integrated DMS-QMS can help?
The integrated DMS-QMS facilitates seamless collaboration among different departments and teams by providing real-time document sharing, commenting, and editing capabilities, fostering cross-functional communication and efficiency.
5. Regulatory Compliance
Industries are subject to stringent regulatory requirements and standards governing quality management practices.
Ensuring that quality documents comply with these regulations requires continuous monitoring and updates, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
How an Integrated DMS-QMS can help?
By incorporating regulatory requirements directly into document templates and workflows, the integrated DMS-QMS ensures compliance at every stage, streamlining regulatory adherence and reducing the risk of non-compliance.
6. Audit Readiness
Organizations must be prepared for audits by regulatory bodies or external certifying agencies.
Gathering and presenting the necessary documentation during audits can be daunting, especially if documents are scattered across disparate systems or are not well-organized.
How an Integrated DMS-QMS can help?
With document tracking, audit trails, and customizable reporting features, the integrated DMS-QMS prepares organizations for audits by providing easy access to documented processes, revisions, and compliance records.
7. Document Retention and Archiving
Compliance standards often dictate specific requirements for document retention and archiving.
Managing the lifecycle of documents, including retention periods and disposal procedures, poses challenges without a structured approach to document management.
How an Integrated DMS-QMS can help?
Automated retention policies and archival features within the integrated DMS-QMS ensure that documents are stored, managed, and disposed of in accordance with regulatory requirements and organizational policies, simplifying retention and archiving processes.
By linking these systems, organizations can establish and manage quality documentation, mitigate compliance risks, and drive continuous improvement initiatives in the most optimized manner. Embracing this integration is the need of the hour for organizations striving to maintain competitiveness, uphold regulatory standards, and achieve excellence in quality management practices.
Smart Food Safe’s One-Stop Solution for QMS Document Compliance
As a prominent provider of software solutions, Smart Food Safe features Smart Docs as an end-to-end digital tool to maintain document compliance within the quality management system in enterprises.
Our integrated quality document management system offers easy access to standard templates and facilitates migration to the latest versions, enhancing your document control experience. With streamlined document creation, editing, and organization through an intuitive interface and seamless cloud storage integration, Smart Docs simplifies your workflow. Centralized document management, customizable folder structures, and advanced search filters ensure easy retrieval of critical documents. Task scheduling, automated workflows, traceable audit trails, and smart linking capabilities further enhance productivity, accountability, and regulatory compliance.

Quality and Food Safety Management Software
Food Safety and Quality Management Software to streamline processes, track compliance, ensure traceability and maintain audit readiness with global quality and food safety standards


