Smart Food Safe participating in SQF Unites 2025, from March 2nd - 5th, 2025 at the Hyatt Regency, Orlando, Florida. Meet us at Booth #16 .
Smart Food Safe participating in SQF Unites 2025, from March 2nd - 5th, 2025 at the Hyatt Regency, Orlando, Florida. Meet us at Booth #16 .
Smart Food Safe participating in SQF Unites 2025, from March 2nd - 5th, 2025 at the Hyatt Regency, Orlando, Florida. Meet us at Booth #16 .
Smart Food Safe participating in SQF Unites 2025, from March 2nd - 5th, 2025
at the Hyatt Regency, Orlando, Florida. Meet us at Booth #16 .


Smart Food Safe participating in
Petfood Forum 2025, from April 28th to 30th in Kansas City, Missouri. Meet us at Booth #910.
Food Safety Management
Due Diligence in Food Safety: Safeguarding the Supply Chain Against Human-Induced Risks
Due Diligence in Food Safety: Safeguarding the Supply Chain Against Human-Induced Risks
Arundhathy Shabu
Feb 3, 2023

Food Safety Management
Due Diligence in Food Safety: Safeguarding the Supply Chain Against Human-Induced Risks
Arundhathy Shabu
Feb 3, 2023
Due Diligence in Food Safety: Safeguarding the Supply Chain Against Human-Induced Risks
Food Safety Management

Arundhathy Shabu
.
Feb 3, 2023
Have you ever heard the idiom, ‘To err is human’? Being human means we all make mistakes, and we are expected to learn from them. But some human errors made in regard to food safety practices could cost severe consequences for consumer health and food companies.
Hence, relying too much on humans might lead to human errors, which can sometimes culminate in a scenario beyond repair. Some examples of human error that can happen in a food processing setting would be the imprecise reading of instructions, wrong tool usage, performing a process or activity incorrectly or not at the designated time, or lack of a proper food safety culture.
These human errors can be categorized as intentional and unintentional, or accidental. Just as the name suggests, intentional human errors are ones committed with an intention for a profitable cause, whereas unintentional human errors have no particular motivation or pre-planning and can occur due to multiple reasons. Both types of mistakes can ultimately have legal and regulatory repercussions.
The accurate approach to tackling food safety issues caused due to human error is building a foolproof food safety and quality system where a human mistake can be identified or eliminated before any adverse outcome, and the problem can be secured. This is where due diligence has a role to play.
Significance of Due Diligence for Proper Monitoring and Verification
Due diligence in food safety simply means demonstrating proof that the food business has undertaken all the necessary protocols to prevent food safety violations by implementing proper food safety practices for every component of the food production chain.
According to Food Safety Act 1990, an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, food safety due diligence defense concerns people charged who can prove to have taken all reasonable precautions to avoid the commission of the offense by themselves or by a person under their control. This helps food enterprises set up their business in good order and decreases the chances of things going wrong.
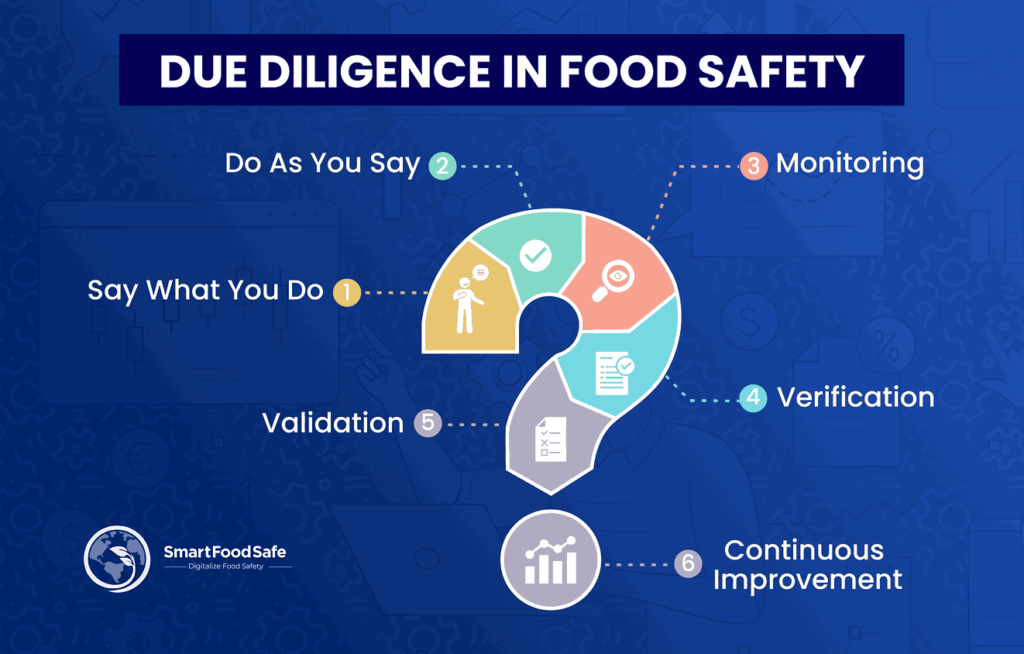
Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) is a powerful tool when it comes to showing due diligence in a food company. This is because the records of your HACCP depict the competence of your food safety system and hygiene practices, along with exhibiting that the food you produce is safe to consume. HACCP system contributes to identifying all probable hazards that can enter the food supply chain and ways to mitigate the hazards in order to produce safe foods. Appropriate execution of HACCP involves monitoring, verification, and validation of the processes as well.
Monitoring is an integral part of a food safety system to evaluate whether established process control points and preventive control points are regulated through real-time observations and measurements. The efficiency of an operational food safety system can be examined through the verification process, which is often associated with a specific time stamp and ensures the system is administered correctly. Validation proves the working of the monitoring activities and the conducted verification procedures, usually referring to a time range. This includes reanalyses and verification audits to bring improvements to the food safety system continuously.
Challenges in Food Industries in Ensuring Proper Monitoring, Verification, and Validation activities
Food industries face several challenges in establishing optimized monitoring, verification, and validation processes to help eliminate food safety issues caused by human error.
- Lack of Know-How: With the evolution of science and technology, the world of food safety is also evolving. Knowing the foundation of food safety requirements and staying updated with food safety hazards and their controls would put the business ahead with risks.
- Employee Awareness: A food safety program can be called working only when the employees are aware of their roles and responsibilities in achieving food safety. Food safety culture demonstrates employees’ engagement in mitigating food safety risks.
- Employee Turnover: High employee turnover, which is very common in food industries, poses one of the biggest risks to training and awareness of food safety expectations.
- Employee Profile: Majority of the food industry workers come from a non-technological background where implementation of new tech-based applications poses significant challenges.
- Resistance to Change: This has been identified as one of the biggest bottlenecks in improving the current practices for better food safety.
- Seasonal workers: Seasonal workers are one of the biggest challenges in the commodity industries, where retaining trained employees has always been the biggest hurdle.
- Nature of Industry: As compared to similar industry categories like Drugs and Natural Health Products, the food industry’s margins remain to be less competitive, which does not allow much room for the business owners to better equip themselves with the food safety system.
- Lack of Tools: Not having the right tools and platform to do the food safety job could cause food safety incidents.
- Cultural and Standard of Living Barriers: Food safety becomes difficult to practice when certain best practices in good manufacturing practices are not followed at home due to cultural or standard of living barriers.
- Management Commitment: Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI) is enforcing food businesses to demonstrate Food Safety Culture and Management commitment due to the fact management must lead by example with food safety.
- Technological Barriers: Having the right technology platform designed from a food safety focused point of view, keeping in mind the majority of the food processors’ profiles.
Overcoming these challenges is a must to illustrate that the food enterprises are in compliance with the established food safety standards and are doing what they are supposed to do as per due diligence, that is, say what you do and do as you say.
Food Safety Management Software
Boost your food business’s hygiene standards with Smart Food Safe’s tech-driven solutions—streamline 4C processes to yield optimal results, and ensure compliance effortlessly.

Food Safety Management Software
Boost your food business’s hygiene standards with Smart Food Safe’s tech-driven solutions—streamline 4C processes to yield optimal results, and ensure compliance effortlessly.
Tech-Enabled Solutions to Resolve Human Errors in Food Supply Chain and Maintain Due Diligence
A transition to tech-enabled solutions to handle the elaborate operations in the food supply chain is an excellent route for managing due diligence while minimizing and preventing food safety incidents due to human-made mistakes. SmartFoodSafe delivers innovative software products that can facilitate establishing an expert food safety system in your organization, which in turn reduces the excessive dependence on human abilities and assists in carrying out food safety practices. Our modules provide features such as scheduling, notification, audit log, workflow, reporting, training, and many more, which can contribute to exercising due diligence effectively.
Scheduling
Instead of relying solely on memory, factory operators can use scheduling tools to assign specific time periods for different production processes and other resource management activities and keep track of one-time or recurring tasks. As tasks are scheduled, they are automatically added to the assigned user’s built-in user calendar as well as sent by email to be added to their email calendar. Scheduling helps avoid issues due to personnel forgetting to carry out an instruction. In addition, the automated scheduling system can aid in decreasing the dependency on staff to carry out time-consuming tasks.
Notification
In case you need a reminder to carry out any actions, the notification feature can be utilized to stay updated on the current and pending actions. The configurable notification capability lets the user decide when and how a user needs to be notified for which actions by email, SMS, or through in-app notifications. Using this tool, the operator will never miss out on a task.
Audit Log
The audit log records function performed by each personnel and provide real-time access to transactions in record keeping. An audit log enables the user to track each and every activity done to review prior changes and make new modifications.
Workflow
Workflow is a feature that enables the digital transfer of documents from one location to another effortlessly, as the user can assign how each document needs to move digitally. Workflow can also help bring real-time transparency to the entire document management system and provide access authority to different personnel as assigned.
Reporting
Custom reporting tools help you monitor compliance and trends and provide a summary of the executed operations, which can be important while conducting verification and validation. This feature is highly customizable according to the needs of each food company through various representation modes such as pie charts, bar graphs, etc, to streamline the reporting process.
Training
The easiest way to eliminate human error-related food safety issues is through making the personnel undergo proper training about the various food safety standards and proactive actions to be executed to minimize the risks to a safe level. Our training software can schedule, assign and manage training requirements with self-learning and group-learning options for different groups of employees.
Any practical activity or process within a food enterprise comprises a certain margin of human error. This is why food companies need to incorporate digitalized applications whenever and wherever possible for an enhanced food supply chain by dodging the hurdles posed by human error and bias, and SmartFoodSafe enables you to do it with ease and cost-effectively.
FAQ
Due diligence in food safety refers to the proactive and responsible actions taken by food businesses to identify, understand, and mitigate risks related to food safety. It involves implementing appropriate measures, conducting regular inspections, maintaining records, and staying updated on regulations to ensure the safety of the food products they produce or handle.
Due diligence in health and safety refers to the legal and moral responsibility of individuals or organizations to take all reasonable measures to prevent harm or injury in the workplace. It involves conducting risk assessments, implementing safety policies and procedures, providing adequate training and resources, and regularly reviewing and improving health and safety practices to ensure a safe and healthy environment for all.

Quality and Food Safety Management Software
Food Safety and Quality Management Software to streamline processes, track compliance, ensure traceability and maintain audit readiness with global quality and food safety standards
Have you ever heard the idiom, ‘To err is human’? Being human means we all make mistakes, and we are expected to learn from them. But some human errors made in regard to food safety practices could cost severe consequences for consumer health and food companies.
Hence, relying too much on humans might lead to human errors, which can sometimes culminate in a scenario beyond repair. Some examples of human error that can happen in a food processing setting would be the imprecise reading of instructions, wrong tool usage, performing a process or activity incorrectly or not at the designated time, or lack of a proper food safety culture.
These human errors can be categorized as intentional and unintentional, or accidental. Just as the name suggests, intentional human errors are ones committed with an intention for a profitable cause, whereas unintentional human errors have no particular motivation or pre-planning and can occur due to multiple reasons. Both types of mistakes can ultimately have legal and regulatory repercussions.
The accurate approach to tackling food safety issues caused due to human error is building a foolproof food safety and quality system where a human mistake can be identified or eliminated before any adverse outcome, and the problem can be secured. This is where due diligence has a role to play.
Significance of Due Diligence for Proper Monitoring and Verification
Due diligence in food safety simply means demonstrating proof that the food business has undertaken all the necessary protocols to prevent food safety violations by implementing proper food safety practices for every component of the food production chain.
According to Food Safety Act 1990, an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, food safety due diligence defense concerns people charged who can prove to have taken all reasonable precautions to avoid the commission of the offense by themselves or by a person under their control. This helps food enterprises set up their business in good order and decreases the chances of things going wrong.
Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) is a powerful tool when it comes to showing due diligence in a food company. This is because the records of your HACCP depict the competence of your food safety system and hygiene practices, along with exhibiting that the food you produce is safe to consume. HACCP system contributes to identifying all probable hazards that can enter the food supply chain and ways to mitigate the hazards in order to produce safe foods. Appropriate execution of HACCP involves monitoring, verification, and validation of the processes as well.
Monitoring is an integral part of a food safety system to evaluate whether established process control points and preventive control points are regulated through real-time observations and measurements. The efficiency of an operational food safety system can be examined through the verification process, which is often associated with a specific time stamp and ensures the system is administered correctly. Validation proves the working of the monitoring activities and the conducted verification procedures, usually referring to a time range. This includes reanalyses and verification audits to bring improvements to the food safety system continuously.
Challenges in Food Industries in Ensuring Proper Monitoring, Verification, and Validation activities
Food industries face several challenges in establishing optimized monitoring, verification, and validation processes to help eliminate food safety issues caused by human error.
- Lack of Know-How: With the evolution of science and technology, the world of food safety is also evolving. Knowing the foundation of food safety requirements and staying updated with food safety hazards and their controls would put the business ahead with risks.
- Employee Awareness: A food safety program can be called working only when the employees are aware of their roles and responsibilities in achieving food safety. Food safety culture demonstrates employees’ engagement in mitigating food safety risks.
- Employee Turnover: High employee turnover, which is very common in food industries, poses one of the biggest risks to training and awareness of food safety expectations.
- Employee Profile: Majority of the food industry workers come from a non-technological background where implementation of new tech-based applications poses significant challenges.
- Resistance to Change: This has been identified as one of the biggest bottlenecks in improving the current practices for better food safety.
- Seasonal workers: Seasonal workers are one of the biggest challenges in the commodity industries, where retaining trained employees has always been the biggest hurdle.
- Nature of Industry: As compared to similar industry categories like Drugs and Natural Health Products, the food industry’s margins remain to be less competitive, which does not allow much room for the business owners to better equip themselves with the food safety system.
- Lack of Tools: Not having the right tools and platform to do the food safety job could cause food safety incidents.
- Cultural and Standard of Living Barriers: Food safety becomes difficult to practice when certain best practices in good manufacturing practices are not followed at home due to cultural or standard of living barriers.
- Management Commitment: Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI) is enforcing food businesses to demonstrate Food Safety Culture and Management commitment due to the fact management must lead by example with food safety.
- Technological Barriers: Having the right technology platform designed from a food safety focused point of view, keeping in mind the majority of the food processors’ profiles.
Overcoming these challenges is a must to illustrate that the food enterprises are in compliance with the established food safety standards and are doing what they are supposed to do as per due diligence, that is, say what you do and do as you say.
Food Safety Management Software
Boost your food business’s hygiene standards with Smart Food Safe’s tech-driven solutions—streamline 4C processes to yield optimal results, and ensure compliance effortlessly.

Tech-Enabled Solutions to Resolve Human Errors in Food Supply Chain and Maintain Due Diligence
A transition to tech-enabled solutions to handle the elaborate operations in the food supply chain is an excellent route for managing due diligence while minimizing and preventing food safety incidents due to human-made mistakes. SmartFoodSafe delivers innovative software products that can facilitate establishing an expert food safety system in your organization, which in turn reduces the excessive dependence on human abilities and assists in carrying out food safety practices. Our modules provide features such as scheduling, notification, audit log, workflow, reporting, training, and many more, which can contribute to exercising due diligence effectively.
Scheduling
Instead of relying solely on memory, factory operators can use scheduling tools to assign specific time periods for different production processes and other resource management activities and keep track of one-time or recurring tasks. As tasks are scheduled, they are automatically added to the assigned user’s built-in user calendar as well as sent by email to be added to their email calendar. Scheduling helps avoid issues due to personnel forgetting to carry out an instruction. In addition, the automated scheduling system can aid in decreasing the dependency on staff to carry out time-consuming tasks.
Notification
In case you need a reminder to carry out any actions, the notification feature can be utilized to stay updated on the current and pending actions. The configurable notification capability lets the user decide when and how a user needs to be notified for which actions by email, SMS, or through in-app notifications. Using this tool, the operator will never miss out on a task.
Audit Log
The audit log records function performed by each personnel and provide real-time access to transactions in record keeping. An audit log enables the user to track each and every activity done to review prior changes and make new modifications.
Workflow
Workflow is a feature that enables the digital transfer of documents from one location to another effortlessly, as the user can assign how each document needs to move digitally. Workflow can also help bring real-time transparency to the entire document management system and provide access authority to different personnel as assigned.
Reporting
Custom reporting tools help you monitor compliance and trends and provide a summary of the executed operations, which can be important while conducting verification and validation. This feature is highly customizable according to the needs of each food company through various representation modes such as pie charts, bar graphs, etc, to streamline the reporting process.
Training
The easiest way to eliminate human error-related food safety issues is through making the personnel undergo proper training about the various food safety standards and proactive actions to be executed to minimize the risks to a safe level. Our training software can schedule, assign and manage training requirements with self-learning and group-learning options for different groups of employees.
Any practical activity or process within a food enterprise comprises a certain margin of human error. This is why food companies need to incorporate digitalized applications whenever and wherever possible for an enhanced food supply chain by dodging the hurdles posed by human error and bias, and SmartFoodSafe enables you to do it with ease and cost-effectively.
FAQ
Due diligence in food safety refers to the proactive and responsible actions taken by food businesses to identify, understand, and mitigate risks related to food safety. It involves implementing appropriate measures, conducting regular inspections, maintaining records, and staying updated on regulations to ensure the safety of the food products they produce or handle.
Due diligence in health and safety refers to the legal and moral responsibility of individuals or organizations to take all reasonable measures to prevent harm or injury in the workplace. It involves conducting risk assessments, implementing safety policies and procedures, providing adequate training and resources, and regularly reviewing and improving health and safety practices to ensure a safe and healthy environment for all.

Quality and Food Safety Management Software
Food Safety and Quality Management Software to streamline processes, track compliance, ensure traceability and maintain audit readiness with global quality and food safety standards


