 English
▾
English
▾
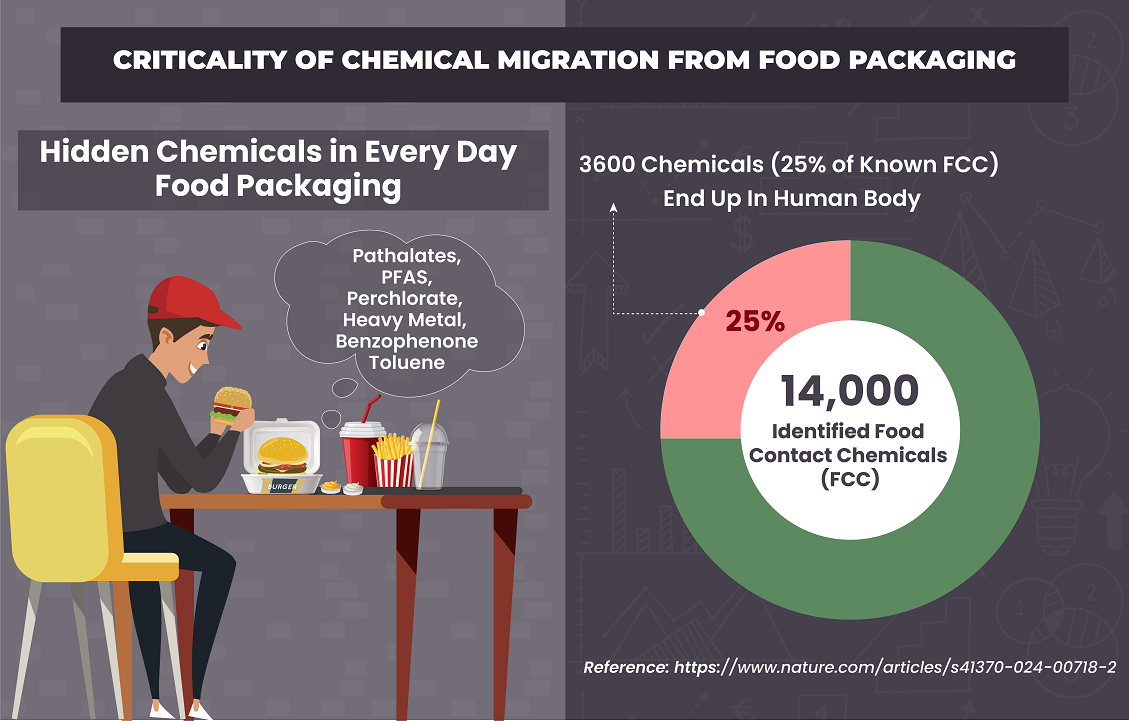
Are you aware that more than 3,600 chemicals out of the identified 14,000 distinct food contact chemicals, that is 25% of the known FCC, leach into food during the manufacturing, processing, packaging, and storage of the world’s food supply, ending up in the human body?
A recent study revealed this fact, demonstrating that such a staggering number indicates that the FCC is a significant source of chemicals for human exposure. Furthermore, 79 of the FCC found in the body are known to cause cancer, genetic mutations, endocrine and reproductive issues, and other health concerns.
While food packaging serves to guarantee food product safety and quality, enhancing shelf life and convenience for consumers, safeguarding the food from the migration of chemicals from food packaging materials is of great concern. This knowledge should be thoroughly understood by relevant stakeholders in the food industry, enabling them to undertake effective measures to mitigate the food safety risks associated with food packaging.
Overview of Migration of Chemicals in Food Packaging
Migration of chemicals in food packaging occurs when chemical compounds are transferred from packaging film through diffusion upon contact with the food. The chemical substances can potentially come from packaging substrates such as paper, cardboard, or plastics, but other packaging components such as printing inks, adhesives, or coatings could also be sources of chemical migrants.
Given below are the most common chemicals posing migration risks in food packaging and corresponding health impacts:
- Phthalates: are used as plasticizers in flexible plastic packaging materials, like PVC (polyvinyl chloride). They are known endocrine disruptors, meaning they can interfere with the body’s hormonal systems, potentially leading to reproductive and developmental health issues.
- Bisphenol A (BPA): is commonly used in the production of polycarbonate plastics and epoxy resins, which are used in food and beverage containers and as a lining for metal cans. BPA is also an endocrine disruptor and has been linked to several health concerns, including heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
- Mineral Oil Hydrocarbons (MOH): can migrate from recycled cardboard packaging into food, especially dry foods like rice, pasta, and cereals. MOHs have been linked to potential liver and lymph node damage and may pose a carcinogenic risk.
- Heavy Metals: including lead, cadmium, and mercury, can migrate from certain types of packaging materials, such as inks, dyes, or coatings. These metals are highly toxic and can accumulate in the body, leading to various chronic health conditions, including neurological disorders and kidney damage.
- Formaldehyde: is sometimes used in the manufacturing of plastic packaging. Prolonged exposure to this chemical has been linked to cancer and respiratory issues.
When selecting packaging materials for a particular food product, it is essential to consider the ingredients of the product and their potential interactions with the packaging, as well as the impact on food quality and safety.
Key Factors Influencing the Chemical Migration Process
Chemical migration from packaging to food is influenced by several key factors:
- Nature of Food: The type and composition of food play a significant role in migration. Fatty foods, for example, show higher levels of migration. Studies often use food simulants to evaluate how food properties affect the process.
- Type of Contact: Direct contact between food and packaging increases migration rates, while indirect contact, where a gas layer separates them, results in slower migration.
- Duration of Contact: The longer food is in contact with packaging, the greater the migration. Research shows that migration increases with time, following a pattern proportional to the square root of the contact duration.
- Temperature: Higher temperatures accelerate migration, as the balance between food and packaging is reached faster.
- Packaging Material: The thickness and type of packaging material affect migration. The thickness and the plasticization of the packaging material affect the migration of specific additives such that thick packaging slows migration, whereas thinner packaging allows greater migration.
- Migrant Characteristics: The properties of the migrating substance—like volatility, molecular weight, and molecular structure—impact the migration rate. Lighter, more volatile substances migrate faster, while larger, branched molecules migrate slower.
- Concentration in Packaging: The driving force behind migration is the concentration gradient, where chemicals move from areas of higher concentration in the packaging material to lower concentration in the food.
The primary criterion for choosing food packaging should always be adherence to current laws and regulations, which will take into consideration these influencing characteristics. Various levels of safety standards for FCC are practiced from the country level to the regional level, along with some certification programs, such as the Global Food Safety Initiative, contributing to the same.
Regulatory Frameworks Established for Food Packaging Safety
Various regulatory bodies around the world have established guidelines and regulations to control the safety of food packaging materials and limit the migration of harmful chemicals. Compliance with these regulations is paramount for all stakeholders involved in food production, packaging, and distribution.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA): In the United States, the FDA is responsible for regulating food packaging materials under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C Act). The FDA establishes limits on the use of certain substances in packaging materials and requires that manufacturers demonstrate that these materials are safe for contact with food. Specific migration limits (SMLs) are often set for substances that pose a risk to human health.
- European Union (EU) Regulations: The EU has developed strict regulations governing food contact materials (FCMs) through Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004. This regulation applies to all materials and articles intended to come into contact with food. It mandates that FCMs must not transfer their constituents to food in quantities that could endanger human health or alter the food’s composition, taste, or smell.
- Health Canada and the Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA): In Canada, the regulatory framework for packaging materials is governed by the Food and Drugs Act (F&D Act) and the Food and Drug Regulations (FDRs). Section 4 of the F&D Act prohibits the sale of food that contains harmful substances, is unfit for consumption, is filthy or decomposed, is adulterated, or is handled under unsanitary conditions.
- Other Global Standards: Countries like Malaysia, Japan, Australia, China, and South Africa also have their regulatory frameworks for food contact materials, often influenced by the guidelines established by Codex Alimentarius, a global food safety standards organization.
Best Practices for Mitigating Chemical Migration Risks
To ensure that food packaging materials do not pose a risk to consumer health, manufacturers, regulators, and food businesses must adopt stringent safety protocols. Below are some best practices to prevent the migration of harmful chemicals into food products.
Use of Safer Materials
One of the most effective ways to mitigate the risk of chemical migration is by selecting packaging materials that are less likely to leach harmful substances. Choosing food-grade materials that comply with regulatory standards is the first step in minimizing chemical migration risks. Many companies are transitioning to safer alternatives, such as BPA-free plastics or plant-based biodegradable packaging materials. Glass, although more expensive, is considered one of the safest packaging materials due to its impermeability and inertness.
Adopting Barrier Technologies
Barrier technologies, such as multilayer packaging or coatings, can be used to prevent the migration of harmful chemicals. These barriers act as a protective layer between the packaging material and the food, reducing the chances of contamination. For example, aluminum or silica-based coatings can be applied to plastic packaging to enhance its protective capabilities.
Innovations in Food Packaging
Advancements in nanotechnology and smart packaging offer promising solutions for reducing migration. Nanocomposites, for example, can be incorporated into packaging materials to improve their barrier properties, making them more resistant to chemical leaching. Smart packaging, which includes sensors and indicators, can provide real-time information on the integrity of packaging, helping to detect any contamination risks during storage or transport.
Testing and Monitoring
Routine testing and monitoring of packaging materials for compliance with regulatory limits are crucial to ensuring food safety. Migration tests, conducted under different conditions (e.g., temperature, time, and type of food), help determine the extent to which chemicals may leach into food. These tests can be used to evaluate both the packaging material itself and any printing inks, adhesives, or coatings used.
Control of Manufacturing Processes
Ensuring the cleanliness and control of manufacturing processes is critical to preventing contamination. Packaging materials should be produced in environments that minimize the risk of exposure to external contaminants, such as heavy metals or other chemicals. Since higher temperatures can accelerate chemical migration, it is essential to control the temperature during both packaging production and food storage as well.
Educating Stakeholders
For effective risk mitigation, all stakeholders involved in the food supply chain—packaging manufacturers, food producers, and regulators—must be well-informed about the risks of chemical migration. Training programs, guidelines, and open communication can help ensure that safety measures are implemented and followed at every stage of production.
Recycling and Circular Economy Considerations
The increasing emphasis on sustainability and the use of recycled materials in packaging adds another layer of complexity to the issue of chemical migration. Recycled packaging materials may contain non-intentionally added substances, including contaminants from previous uses. To address this, food companies must ensure that recycled materials used for food packaging undergo thorough testing and comply with regulatory standards.
Strengthen Your Food Packaging Safety Practices with Smart Food Safe
Smart Food Safe’s food safety management modules are equipped with targeted capabilities for appropriate approval strategies to control the migration of chemicals, hence ascertaining the food safety of food packaging materials.
Starting from suppliers involved in food manufacturing, Smart Supplier is a software instrumental to streamlining suppliers’ approval process by allowing companies to set customized criteria for evaluating their packaging materials and ensuring only compliant and safe materials are used in their packaging.
Smart HACCP facilitates the identification and management of potential chemical hazards in food packaging materials by automating HACCP plans and effectively monitoring critical control points (CCPs) associated with chemical migration.
During food manufacturing, food manufacturers can employ Smart Specification to assist in managing the packaging material specifications, including the tracking of chemical compositions and detecting potential hazards present in them.
Smart Audit is a digital solution that enables conducting efficient audits with customizable checklists and automated audit reports to ensure that their food packaging processes adhere to regulatory standards, promptly addressing any compliance issues related to chemical migration.

 French
French
 Spanish
Spanish
 Portuguese
Portuguese
