Smart Food Safe participating in SQF Unites 2025, from March 2nd - 5th, 2025 at the Hyatt Regency, Orlando, Florida. Meet us at Booth #16 .
Smart Food Safe participating in SQF Unites 2025, from March 2nd - 5th, 2025 at the Hyatt Regency, Orlando, Florida. Meet us at Booth #16 .
Smart Food Safe participating in SQF Unites 2025, from March 2nd - 5th, 2025 at the Hyatt Regency, Orlando, Florida. Meet us at Booth #16 .
Smart Food Safe participating in SQF Unites 2025, from March 2nd - 5th, 2025
at the Hyatt Regency, Orlando, Florida. Meet us at Booth #16 .


Smart Food Safe participating in
Petfood Forum 2025, from April 28th to 30th in Kansas City, Missouri. Meet us at Booth #910.
Food Safety Management
Do You Know the 4C’s
of Food Hygiene?
Do You Know the 4C’s
of Food Hygiene?
Arundhathy Shabu
April 24, 2024

Food Safety Management
Do You Know the 4C’s
of Food Hygiene?
Arundhathy Shabu
April 24 , 2024
Do You Know the 4C’s of Food Hygiene?
Food Safety Management

Arundhathy Shabu
.
April 24, 2024
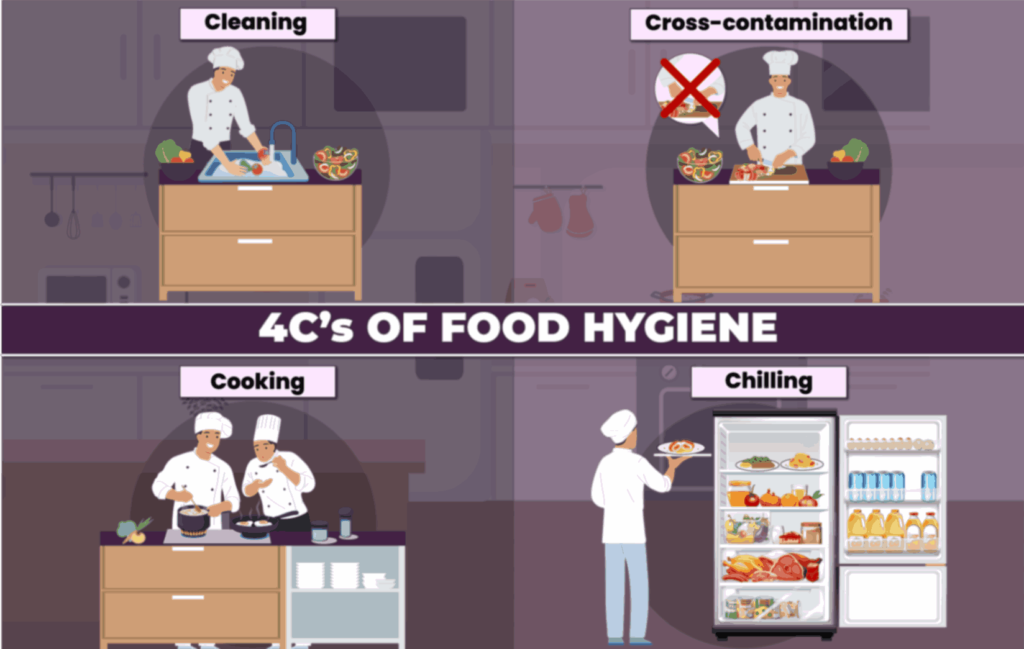
In the food sector, a myriad of food safety practices are taught, yet they often stem from a core set of fundamental principles. Known as the 4Cs of food hygiene, these principles form the cornerstone upon which more advanced food safety measures are built. These include:
- Cleaning
- Cooking
- Chilling
- Cross-contamination
By adhering to these components, we can substantially safeguard consumers from foodborne illnesses and potential food hazards. When implemented correctly, these methods not only enhance food safety but also ensure compliance with a majority of food safety laws and regulations.
Significance of 4Cs of Food Hygiene
Understanding the 4 Cs of food safety holds importance for several reasons:
- They guard against harmful bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms that can lead to foodborne illnesses.
- They provide a straightforward framework that everyone in the food supply chain, from producers to handlers and consumers, can easily grasp and comply.
- They are adaptable to various food production settings, including commercial kitchens, restaurants, and household kitchens.
- They minimize the likelihood of contamination at every stage of food production and reduce the incidence of related hospital cases.
Furthermore, for those involved in food manufacturing, familiarity with the 7 HACCP principles is essential for the effective execution of the 4 Cs of food safety. These HACCP principles focus on identifying and managing food production hazards. Mastering them enables a comprehensive application of the 4 Cs—Clean, Cook, Chill, and Prevent Cross-Contamination—to maintain food safety and ward off illnesses.
Food Safety Management Software
Boost your food business’s hygiene standards with Smart Food Safe’s tech-driven solutions—streamline 4C processes to yield optimal results, and ensure compliance effortlessly.

Food Safety Management Software
Boost your food business’s hygiene standards with Smart Food Safe’s tech-driven solutions—streamline 4C processes to yield optimal results, and ensure compliance effortlessly.
The 4 Cs of Food Hygiene
- Cleaning
Cleaning is a crucial process for eliminating dirt, dangerous bacteria, grease, allergen remnants, and other unwanted substances, thereby preventing their transfer to food.
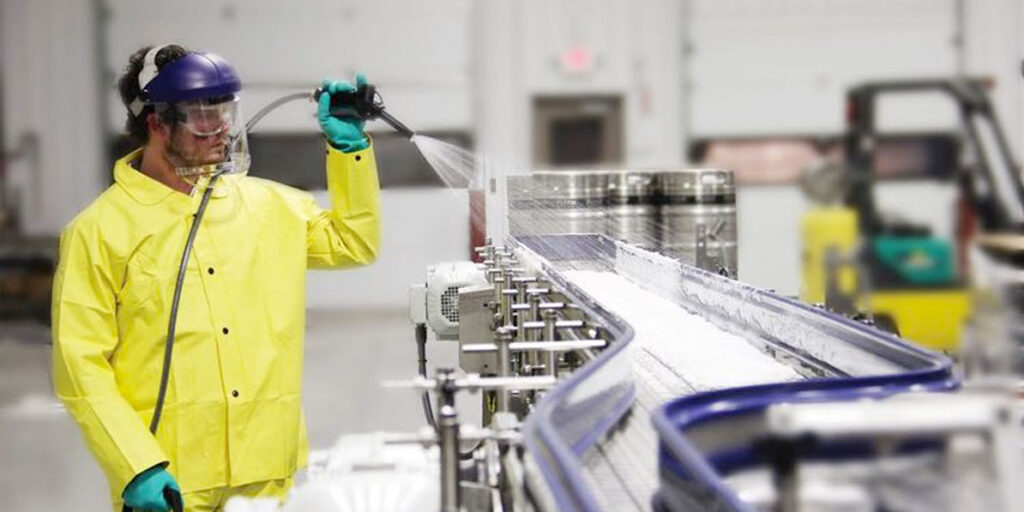

Inadequate cleaning methods can result in the accumulation of dangerous bacteria and the risk of cross-contamination. Therefore, maintaining high cleaning standards ensures a safe environment for food preparation and cooking.Cleaning should be conducted in two phases: cleaning and disinfecting. Cleaning removes dirt and prepares surfaces for disinfection. Disinfecting involves using chemicals to eliminate bacteria. A detergent serves as a general cleaning agent, whereas a disinfectant is designed to kill germs. It is vital to use a detergent prior to applying a disinfectant, as bacteria can be concealed beneath dirt.
Cleaning in a food establishment involves the following aspects:
- Food Contact Surfaces: Keeping food preparation surfaces clean and sanitized is required to prevent microbiological hazards and foodborne illnesses, especially in small kitchens where both raw and cooked food pass through the same area.
- Facilities: Regular cleaning of floors, walls, windows, and doors using appropriate cleaning solutions is necessary. Dust, which can contaminate food and cause spoilage, needs particular attention.
- Raw Materials: Cleaning raw materials involves removing excess soil from root crops, inspecting for debris, and isolating materials that are not wholesome. This reduces spoilage risks and prevents the spread of food safety hazards.
- Equipment: Kitchen equipment should be cleaned and sanitized before and after use to prevent leftover food material from attracting harmful bacteria. Washing with soapy water and rinsing with warm water is recommended.
- Personal Hygiene: Proper handwashing before and after handling foods is key. It should be done correctly for at least 20 seconds using soapy and hot water to kill foodborne bacteria. Employees should also maintain personal hygiene by wearing protective uniforms, clean clothes, tied hair, and trimmed nails.
Consistent cleaning and sanitation across these areas are non-negotiable for establishing a safe and hygienic food establishment.
- Cooking
If food isn’t adequately cooked, it could pose a safety risk when consumed. Complying with the proper cooking and handling practices is paramount to eradicating potentially harmful bacteria.
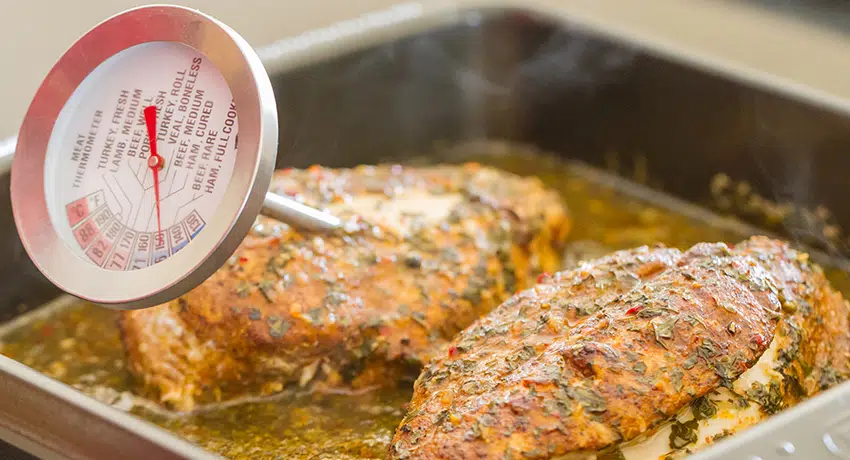

Maintaining precise time and temperature controls guarantees the safety of the food being prepared. Cooking food at the appropriate temperature for the designated duration effectively eradicates harmful bacteria. Typically, when cooking, aim to reach a core temperature of 70°C and maintain it for a minimum of two minutes. This is generally useful in wiping out any germs or bacteria. Alternatively, you can use different combinations of time and temperature to achieve similar results.
To ensure safe and delicious cooking:
- Correctly measure the target temperature using a clean food thermometer and a cooking chart to guide you.
- Follow the prescribed cooking time along with the correct temperature; longer times are needed for lower temperatures.
- Ensure even cooking reaches the correct internal temperature throughout the food, avoiding cold spots.
- Serve food hot, maintaining a temperature of at least 63°C (145°F) to prevent bacterial growth.
- When reheating leftovers, make sure to thoroughly heat them to 74°C (165°F) to ensure they are safe to eat.
- Chilling
Storing foods at chilling temperatures helps maintain their freshness and extends their shelf life. Leaving raw, prepared, and cooked foods at room temperature can lead to rapid bacterial growth, increasing the risk of foodborne illnesses.
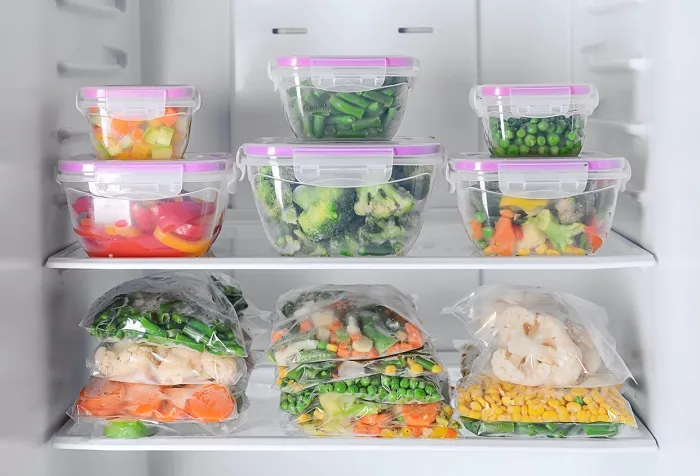

Chilling is a critical food safety measure that helps manage food hazards. The basic idea is that refrigeration’s low temperatures inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria, benefiting both cooked dishes and raw ingredients. It is important to maintain these low temperatures continuously.
When chilling food, keep these key points in mind:
- Refrigerate raw items like meat if they won’t be used right away.
- Store leftovers in the fridge within 2 hours of eating part of them.
- Organize foods in the fridge by type. Separate cooked and ready-to-eat items from raw meats, which should be placed on the bottom shelf to prevent cross-contamination.
- Regularly check and calibrate your fridge thermometer for accurate temperature readings.
- Keep your refrigerator clean.
Before placing food in the fridge, it should be chilled quickly, ideally within the first two hours. This rapid cooling prevents the fridge’s overall temperature from rising, ensuring it can properly cool all items. Proper chilling is key to prolonging food shelf life and storing perishable ingredients for future use.
- Cross-Contamination
Cross-contamination occurs when harmful bacteria are accidentally transferred from one surface to another. For example, if you handle raw meat and then cut vegetables without washing your hands, you could transfer bacteria to the vegetables.

Cross-contamination is one of the quickest routes for pathogens and foodborne illnesses to spread. There are three main types of cross-contamination:
i) Food to food
ii) Equipment to food
iii) People to food
Cross-contamination presents a significant threat to any food establishment. Common scenarios where cross-contamination occurs include:
- Handling raw foods like meat and vegetables without washing hands in between. Since vegetables undergo less processing than meat, pathogens have a higher chance of survival when transferred.
- Using unclean uniforms, protective gear, utensils, and other items that may come into contact with food.
- Allowing ill employees to work. Viruses from sick kitchen staff can also contaminate food and act as a means of disease transmission.
- Using a single cutting board or failing to adequately clean surfaces that come into contact with food during preparation.
- Incorrect handwashing techniques.
The first step to preventing cross-contamination is understanding how and when it can occur. This knowledge enables food handlers to be more vigilant and mindful of their actions. When addressing cross-contamination, it is imperative to consider food allergens as well. Having an allergen matrix and a control plan in place is mandatory.
Coupled with proper monitoring and documentation, these hygiene practices not only guarantee the quality and safety of food products but also fulfill legal requirements. A well-trained food safety team and an effective Food Safety Management System (FSMS), based on the principles of HACCP, are indispensable assets in this regard. By covering segments like the four Cs of food safety, high-risk techniques, allergen control, and supplier approval, an FSMS serves as a living document reflecting current operations and aids in demonstrating compliance during regulatory inspections. Embracing digital solutions for FSMS can expedite the achievement and maintenance of compliance, ultimately fostering success in the competitive landscape of the food industry.
Ensure the 4C’s of Food Hygiene with Smart Food Safe’s Food Safety Management Software
Smart Food Safe‘s food safety management solution helps food businesses maintain high standards of hygiene by providing tech-enabled tools and protocols to assist in ensuring proper cleaning of equipment and surfaces, accurate cooking temperatures, appropriate chilling of perishable foods, and prevention of cross-contamination between raw and cooked items.
By leveraging the platform, organizations can meticulously track and maintain hygiene standards, ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements while fostering consistent practices across operations. Through robust communication features, the software facilitates seamless collaboration among stakeholders, bolstering total food safety measures and promoting trust and confidence in the products delivered to consumers.

Food Safety Management Software
Boost your food business’s hygiene standards with Smart Food Safe’s tech-driven solutions—streamline 4C processes to yield optimal results, and ensure compliance effortlessly.
In the food sector, a myriad of food safety practices are taught, yet they often stem from a core set of fundamental principles. Known as the 4Cs of food hygiene, these principles form the cornerstone upon which more advanced food safety measures are built. These include:
- Cleaning
- Cooking
- Chilling
- Cross-contamination
By adhering to these components, we can substantially safeguard consumers from foodborne illnesses and potential food hazards. When implemented correctly, these methods not only enhance food safety but also ensure compliance with a majority of food safety laws and regulations.
Significance of 4Cs of Food Hygiene
Understanding the 4 Cs of food safety holds importance for several reasons:
- They guard against harmful bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms that can lead to foodborne illnesses.
- They provide a straightforward framework that everyone in the food supply chain, from producers to handlers and consumers, can easily grasp and comply.
- They are adaptable to various food production settings, including commercial kitchens, restaurants, and household kitchens.
- They minimize the likelihood of contamination at every stage of food production and reduce the incidence of related hospital cases.
Furthermore, for those involved in food manufacturing, familiarity with the 7 HACCP principles is essential for the effective execution of the 4 Cs of food safety. These HACCP principles focus on identifying and managing food production hazards. Mastering them enables a comprehensive application of the 4 Cs—Clean, Cook, Chill, and Prevent Cross-Contamination—to maintain food safety and ward off illnesses.
Food Safety Management Software
Boost your food business’s hygiene standards with Smart Food Safe’s tech-driven solutions—streamline 4C processes to yield optimal results, and ensure compliance effortlessly.

The 4 Cs of Food Hygiene
- Cleaning
Cleaning is a crucial process for eliminating dirt, dangerous bacteria, grease, allergen remnants, and other unwanted substances, thereby preventing their transfer to food.

Inadequate cleaning methods can result in the accumulation of dangerous bacteria and the risk of cross-contamination. Therefore, maintaining high cleaning standards ensures a safe environment for food preparation and cooking.Cleaning should be conducted in two phases: cleaning and disinfecting. Cleaning removes dirt and prepares surfaces for disinfection. Disinfecting involves using chemicals to eliminate bacteria. A detergent serves as a general cleaning agent, whereas a disinfectant is designed to kill germs. It is vital to use a detergent prior to applying a disinfectant, as bacteria can be concealed beneath dirt.
Cleaning in a food establishment involves the following aspects:
- Food Contact Surfaces: Keeping food preparation surfaces clean and sanitized is required to prevent microbiological hazards and foodborne illnesses, especially in small kitchens where both raw and cooked food pass through the same area.
- Facilities: Regular cleaning of floors, walls, windows, and doors using appropriate cleaning solutions is necessary. Dust, which can contaminate food and cause spoilage, needs particular attention.
- Raw Materials: Cleaning raw materials involves removing excess soil from root crops, inspecting for debris, and isolating materials that are not wholesome. This reduces spoilage risks and prevents the spread of food safety hazards.
- Equipment: Kitchen equipment should be cleaned and sanitized before and after use to prevent leftover food material from attracting harmful bacteria. Washing with soapy water and rinsing with warm water is recommended.
- Personal Hygiene: Proper handwashing before and after handling foods is key. It should be done correctly for at least 20 seconds using soapy and hot water to kill foodborne bacteria. Employees should also maintain personal hygiene by wearing protective uniforms, clean clothes, tied hair, and trimmed nails.
Consistent cleaning and sanitation across these areas are non-negotiable for establishing a safe and hygienic food establishment.
- Cooking
If food isn’t adequately cooked, it could pose a safety risk when consumed. Complying with the proper cooking and handling practices is paramount to eradicating potentially harmful bacteria.

Maintaining precise time and temperature controls guarantees the safety of the food being prepared. Cooking food at the appropriate temperature for the designated duration effectively eradicates harmful bacteria. Typically, when cooking, aim to reach a core temperature of 70°C and maintain it for a minimum of two minutes. This is generally useful in wiping out any germs or bacteria. Alternatively, you can use different combinations of time and temperature to achieve similar results.
To ensure safe and delicious cooking:
- Correctly measure the target temperature using a clean food thermometer and a cooking chart to guide you.
- Follow the prescribed cooking time along with the correct temperature; longer times are needed for lower temperatures.
- Ensure even cooking reaches the correct internal temperature throughout the food, avoiding cold spots.
- Serve food hot, maintaining a temperature of at least 63°C (145°F) to prevent bacterial growth.
- When reheating leftovers, make sure to thoroughly heat them to 74°C (165°F) to ensure they are safe to eat.
- Chilling
Storing foods at chilling temperatures helps maintain their freshness and extends their shelf life. Leaving raw, prepared, and cooked foods at room temperature can lead to rapid bacterial growth, increasing the risk of foodborne illnesses.

Chilling is a critical food safety measure that helps manage food hazards. The basic idea is that refrigeration’s low temperatures inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria, benefiting both cooked dishes and raw ingredients. It is important to maintain these low temperatures continuously.
When chilling food, keep these key points in mind:
- Refrigerate raw items like meat if they won’t be used right away.
- Store leftovers in the fridge within 2 hours of eating part of them.
- Organize foods in the fridge by type. Separate cooked and ready-to-eat items from raw meats, which should be placed on the bottom shelf to prevent cross-contamination.
- Regularly check and calibrate your fridge thermometer for accurate temperature readings.
- Keep your refrigerator clean.
Before placing food in the fridge, it should be chilled quickly, ideally within the first two hours. This rapid cooling prevents the fridge’s overall temperature from rising, ensuring it can properly cool all items. Proper chilling is key to prolonging food shelf life and storing perishable ingredients for future use.
- Cross-Contamination
Cross-contamination occurs when harmful bacteria are accidentally transferred from one surface to another. For example, if you handle raw meat and then cut vegetables without washing your hands, you could transfer bacteria to the vegetables.

Cross-contamination is one of the quickest routes for pathogens and foodborne illnesses to spread. There are three main types of cross-contamination:
i) Food to food
ii) Equipment to food
iii) People to food
Cross-contamination presents a significant threat to any food establishment. Common scenarios where cross-contamination occurs include:
- Handling raw foods like meat and vegetables without washing hands in between. Since vegetables undergo less processing than meat, pathogens have a higher chance of survival when transferred.
- Using unclean uniforms, protective gear, utensils, and other items that may come into contact with food.
- Allowing ill employees to work. Viruses from sick kitchen staff can also contaminate food and act as a means of disease transmission.
- Using a single cutting board or failing to adequately clean surfaces that come into contact with food during preparation.
- Incorrect handwashing techniques.
The first step to preventing cross-contamination is understanding how and when it can occur. This knowledge enables food handlers to be more vigilant and mindful of their actions. When addressing cross-contamination, it is imperative to consider food allergens as well. Having an allergen matrix and a control plan in place is mandatory.
Coupled with proper monitoring and documentation, these hygiene practices not only guarantee the quality and safety of food products but also fulfill legal requirements. A well-trained food safety team and an effective Food Safety Management System (FSMS), based on the principles of HACCP, are indispensable assets in this regard. By covering segments like the four Cs of food safety, high-risk techniques, allergen control, and supplier approval, an FSMS serves as a living document reflecting current operations and aids in demonstrating compliance during regulatory inspections. Embracing digital solutions for FSMS can expedite the achievement and maintenance of compliance, ultimately fostering success in the competitive landscape of the food industry.
Ensure the 4C’s of Food Hygiene with Smart Food Safe’s Food Safety Management Software
Smart Food Safe‘s food safety management solution helps food businesses maintain high standards of hygiene by providing tech-enabled tools and protocols to assist in ensuring proper cleaning of equipment and surfaces, accurate cooking temperatures, appropriate chilling of perishable foods, and prevention of cross-contamination between raw and cooked items.
By leveraging the platform, organizations can meticulously track and maintain hygiene standards, ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements while fostering consistent practices across operations. Through robust communication features, the software facilitates seamless collaboration among stakeholders, bolstering total food safety measures and promoting trust and confidence in the products delivered to consumers.

Food Safety Management Software
Boost your food business’s hygiene standards with Smart Food Safe’s tech-driven solutions—streamline 4C processes to yield optimal results, and ensure compliance effortlessly.


