 English
▾
English
▾

William Edwards Deming, often hailed as the Father of the Quality Movement, famously said, ‘Improve quality, and you automatically improve productivity.’ This profound insight encapsulates the very essence of total quality management (TQM), a concept of management philosophy focused on a continual quality improvement process of detecting and reducing or eliminating errors to achieve long-term efficiency.
In a TQM initiative, every member of an organization collaborates to enhance processes, products, services, and the organizational culture. Exploring the different aspects of TQM and applying its core principles to industry operations can be key to transforming the end-to-end quality levels of enterprises.
Comprehending Total Quality Management (TQM)
TQM refers to an ongoing effort employed to streamline supply chain management, advance customer service, and ensure that employees receive adequate training. The primary goal is to elevate the quality of an organization’s outputs, including goods and services, by constantly improving internal processes.
TQM incorporates principles and practices from various fields, including:
- Behavioral sciences
- Analysis of both quantitative and qualitative data
- Economic theories
- Process analysis
TQM typically adheres to eight guiding principles, which include an emphasis on customers, a commitment to continuous improvement, and adherence to established processes. It is a structured approach to comprehensive organizational management.
The standards established within the TQM framework can reflect both the organization’s internal priorities and the prevailing industry standards. These industry standards, which may vary across different levels, often include compliance with various laws and regulations specific to the business’s operations.
A Quick Background on TQM
Given below is a timeline breakdown of the initiation and evolution of TQM:
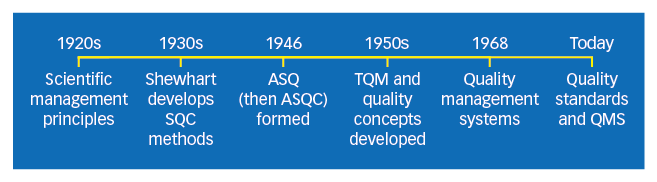
Reference: https://asq.org/quality-resources/total-quality-management/tqm-history
1920s
⇒ Early Quality Management
The principles of scientific management influenced U.S. industry, separating planning and execution. Union opposition grew due to workers losing input on work conditions. The Hawthorne experiments revealed that worker participation improved productivity.
1930s
⇒ Statistical Quality Control
Walter Shewhart developed methods for statistical analysis and quality control.
1950s
⇒ TQM Foundations
- W. Edwards Deming: Taught statistical quality control to Japanese engineers and executives, marking the start of TQM.
- Joseph M. Juran: Introduced quality control and managerial breakthrough concepts.
- Armand V. Feigenbaum: Published “Total Quality Control,” a precursor to TQM.
- Philip B. Crosby: Promoted zero defects, enhancing quality improvement in many companies.
1968
⇒ Japanese Quality Control
The Japanese named their approach “companywide quality control,” leading to the concept of quality management systems. Kaoru Ishikawa’s work contributed to Japan’s leadership in quality.
Today
⇒ Modern TQM
TQM represents a broad approach to managing organizational quality. Standards like ISO 9000 and awards such as the Deming Prize and Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award outline TQM principles and processes. The term TQM is less commonly used now due to the development of international quality management standards.
Key 8 Elements of TQM
TQM integrates strategy, data, and effective communication to embed quality into the organization’s culture and activities. The following are the 8 key elements of TQM:
- Customer-focused: The level of quality is ultimately determined by the customer. Regardless of the organization’s efforts to improve quality—be it through employee training, quality integration in design, or technological upgrades—the customer’s perception of these efforts determines their success.
- Total Employee Involvement: Every employee works towards common goals with full commitment. Achieving total employee commitment requires eliminating workplace fear, empowering employees, and providing a conducive environment. High-performance work systems merge continuous improvement with regular business operations, with self-managed work teams being a form of empowerment.
- Process-Centered: TQM emphasizes process thinking. A process involves steps that transform inputs from suppliers (internal or external) into outputs delivered to customers (internal or external). These steps are clearly defined, and performance is continuously monitored to detect variations.
- Integrated System: TQM focuses on the horizontal processes that interconnect different functional specialties within an organization. Micro-processes combine into larger processes, which aggregate into business processes essential for strategy implementation. Everyone should understand the organization’s vision, mission, guiding principles, quality policies, objectives, and critical processes. An integrated business system, possibly modeled after the Baldrige Award criteria or ISO 9000 standards, connects all improvement elements to exceed stakeholder expectations.
- Strategic and Systematic Approach: Managing quality involves a strategic and systematic approach to achieving the organization’s vision, mission, and goals. This approach, known as strategic planning or management, includes creating a strategic plan that incorporates quality as a core component.
- Continual Improvement: Central to TQM is the concept of continual process improvement, which drives the organization to be both analytical and creative in enhancing competitiveness and effectiveness in meeting stakeholder expectations.
- Fact-Based Decision Making: TQM relies on data collection and analysis to measure performance, improve decision-making accuracy, achieve consensus, and predict future outcomes based on historical data.
- Effective Communications: Effective communication is crucial during organizational changes and daily operations. It helps maintain morale and motivate employees at all levels through well-planned strategies, methods, and timely communication.
Advantages Put Forth by TQM
TQM brings forward a wide range of benefits including:
Implementation of the TQM System
Setting up a TQM system is a unique journey for each organization. There is no one-size-fits-all solution; rather, the strategy must be tailored to the specific culture, management practices, and processes of the organization. Nevertheless, the following are the basic steps involved in the generic strategy of TQM implementation:
- Identify Company Culture and Values: Begin by identifying your company’s existing culture, core values, and systems. Use this information to create a master plan tailored to your organization.
- Communication of Core Values: Top management must commit to TQM, recognizing it as a strategic priority, and communicate core values and principles that will guide the TQM efforts.
- Assess Current State: The organization should assess its current culture, customer satisfaction, and existing quality management systems.
- Develop a Master Plan: Based on the assessment, a TQM master plan should be developed, outlining the steps for implementation.
- Identify Customer Demands: The organization must identify and prioritize customer demands, ensuring products and services are aligned to meet these needs.
- Map Critical Processes: Management should map out critical processes that help meet customer needs.
- Form Improvement Teams: Teams should be formed to focus on process improvement efforts, ensuring that every part of the organization is working towards the same quality goals.
- Steering Committee: A steering committee should manage the momentum of the TQM effort, keeping it on track. Managers should contribute individually through strategic planning, training, coaching, and other methods.
- Evaluate Progress: Daily process management and standardization should take place to maintain quality. Regular evaluation of progress is essential, with plans revised as needed.
- Employee Awareness and Recognition: Constant awareness and feedback should be provided to employees, and a reward/recognition process should be established to motivate and acknowledge efforts.
TQM implementation can be greatly augmented with tech-assisted, digital, or intelligent quality management solutions, integrating real-time data analytics, IoT sensors, and AI-driven insights to monitor and control quality processes meticulously.
For example, IoT sensors can continuously track production parameters, immediately flagging deviations that could affect product quality. AI algorithms can predict potential quality issues based on historical data, allowing preemptive actions to be taken. Digital platforms enable centralized documentation and instant access to quality records, facilitating audits and compliance with standards like ISO 9001.
Automated TQM workflows ensure that corrective actions are swiftly implemented and tracked, improving overall process efficiency and reducing the risk of human error, in turn, running a holistic and proactive quality management system.
Qualsmart.ai: Usher New Paradigm of TQM with Smart Food Safe’s Quality Management Solution
Embrace the future of TQM in global enterprises with Qualsmart.ai, Smart Food Safe’s pioneering all-in-one quality management solution designed to revolutionize the different aspects of quality protocols. Leveraging advanced AI technologies and comprehensive data analytics, Qualsmart.ai offers real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and automated compliance reporting through a well-built range of modules.
Having a provision to seamlessly integrate with existing systems, Qualsmart.ai empowers organizations to diligently manage quality processes, reduce risks, and achieve operational excellence. Experience a new era of efficiency and reliability in quality management with Qualsmart.ai, where innovation meets quality compliance.

 French
French
 Spanish
Spanish
 Portuguese
Portuguese
