 English
▾
English
▾

Are you aware that 1 in 8 people in the world was living with obesity in 2022, such that 2.5 billion adults and over 390 million children and adolescents were overweight, as released by the World Health Organization on 1st March 2024?
Obesity is a medical condition characterized by excessive body fat accumulation, significantly impacting lifestyle by increasing the risk of various health issues such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and mobility limitations.
When food businesses provide access to calorie counts and other relevant nutritional data through menu labeling, individuals can make more informed choices about their meals, opting for healthier options and controlling portion sizes, creating awareness to support consumers in maintaining a healthy weight and reducing the risk of obesity-related health issues.
What is Menu Labeling?
Menu labeling involves the inclusion of nutritional information directly on menus and menu boards. Serving as an educational tool, it aids in fostering healthier dietary choices among consumers, ultimately contributing to improved overall health. Typically, menu labeling conveys details such as calorie counts, levels of saturated fat, sodium content, and carbohydrates present in menu items.
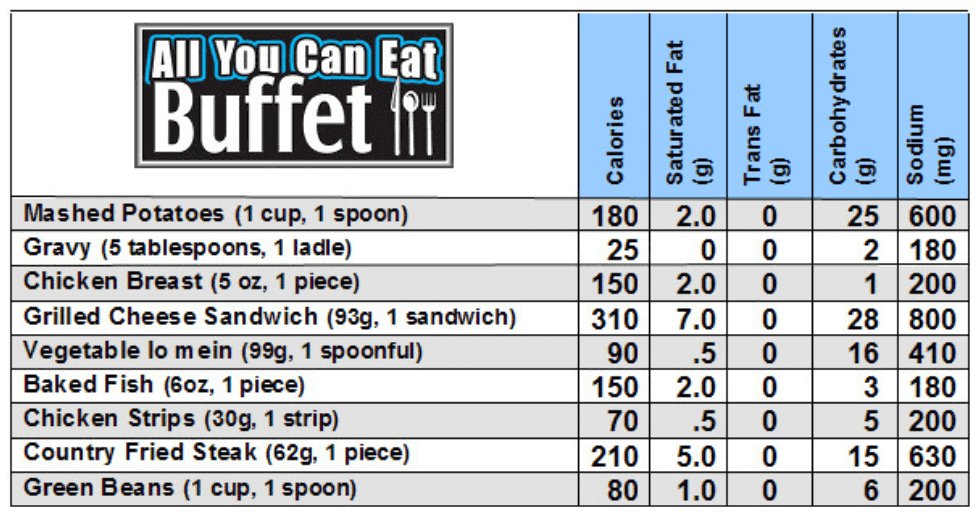
Reference: https://www.sigmatest.org/news/fssai-makes-menu-labeling-mandatory-for-restaurants/
Importance of Menu Labeling
Dining out in general contributes to increased obesity through several factors::
- Restaurants entice patrons with enticing menu visuals and TV ads, leading them to opt for seemingly healthy choices that are often deceiving.
- Restaurant dishes often pack a staggering number of calories, with some entrees exceeding 1,000 calories. Considering that most adults aim for a daily intake of 2,000 calories, these oversized portions facilitate overconsumption.
- Chain restaurant menus typically lack whole-grain options, which are rich in fiber and promote satiety. Conversely, refined white flour items digest quickly, causing hunger to return sooner.
- Unhealthy food items like burgers and fries are often more affordable than healthier alternatives like salads and fruits, incentivizing patrons to make less nutritious choices.
In dining-out scenarios, individuals often underestimate the calorie content of the dishes they consume. This habit can contribute to weight gain and obesity, leading to various health issues like heart diseases, cancers, diabetes, and strokes. By being well-informed, consumers can opt for lower-calorie options both for themselves and their children.
Menu labeling holds particular significance in safeguarding the health of children, considering the alarming rise in childhood obesity rates. Furthermore, individuals with specific dietary requirements, high blood pressure, or diabetes must be aware of food contents to prevent immediate health complications. Hence, menu labeling serves as a vital tool for ensuring informed choices and promoting better health outcomes.
Overview of Guidelines for Menu Labeling Compliance
Menu labeling compliance varies by region, reflecting different priorities and approaches to public health and consumer protection. Below is a quick glimpse at the scenario of informational labeling in different regions around the world:
Canada:
The menu labeling regulations in Canada are primarily under provincial jurisdiction, resulting in some variability across provinces. For example, Ontario’s Healthy Menu Choices Act, 2015, and its accompanying regulation (O. Reg 50/16) (“HMCA”) came into effect on January 1st, 2017, requiring regulated food service premises to post calories for the food and drink items they serve.

Reference: https://files.ontario.ca/moh-hmca-fact-sheet-restaurants-en-2023-03-07.pdf
Europe:
The EU law on food information to consumers necessitates the provision of food information in order to pursue a high level of protection of consumers’ health and interests by providing a basis for final consumers to make informed choices and to make safe use of food, with particular regard to health, economic, environmental, social and ethical considerations. Anyhow, comprehensive data on specific menu labeling requirements remains scarce.
Australia:
The menu labeling setting in Australia involves a historical backdrop where in 2011, the Australia and New Zealand Food Regulation Ministerial Council agreed on principles for implementing point-of-sale nutrition information, though these were not uniformly adopted across jurisdictions. In 2019, acknowledging the need for national consistency, Food Ministers aimed to develop a regulatory measure under the Australia-New Zealand Food Standards Code. This involved the creation of Ministerial Policy Guidelines applicable to both countries. These guidelines seek to inform the development of a framework for menu labeling that minimizes inconsistency, ensures fairness among businesses, and facilitates healthier food choices for consumers at the point of sale.
UAE:
Menu labeling regulations have been established by the Dubai Muncipality in ‘Calorie Declaration and Healthy Claims in Food Service Establishments’ to ensure transparency and accuracy in the representation of nutritional information for consumers. Any food or menu item that makes claims regarding calorie or other nutrient content must be backed by supporting documentation. This includes lab analysis, nutritional analysis, or nutrition calculation. All claims made by food service establishments must be substantiated, and they should be prepared to justify these claims when required by Dubai Municipality. In situations where there may be opposing evidence or opinions, the burden lies with the establishment to demonstrate that their claims are valid and supported by credible data.
United States of America:
The menu labeling regulations for the U.S. were established by the U.S. FDA and become applicable for restaurants and similar retail food establishments that are part of a chain of 20 or more locations doing business under the same name and offering for sale substantially the same menu items. These enterprises are required to consistently display calorie information for numerous menu items nationwide and provide additional nutritional information in writing upon request. Given below is a concise overview of the menu labeling final rule, with the reference from National Restaurant Association:
⇒ Food & Beverage Items Requiring Menu Labeling
(As per US FDA) Standard menu items refer to permanent menu items; seasonal items displayed for less than 60 days and test items available for fewer than 90 consecutive days for consumer acceptance testing are exempt. Generally covered foods include standard menu items such as alcoholic beverages, combination meals, variable menu items, food on display, and self-service food and beverages. Generally not covered are daily specials, temporary or seasonal food items, and food involved in customary market testing.
⇒ Nutrition Information to be Provided
Food businesses must:
- Disclose calorie details on menus and menu boards for standard menu items.
- Display a succinct statement concerning suggested daily caloric intake on menus and menu boards, stating, “2,000 calories a day is used for general nutrition advice, but calorie needs vary.”
- Post on menus and menu boards a statement that written nutrition information is available upon request.
The written nutrition information for standard menu items encompasses:
- Total calories
- Calories from fat
- Total fat
- Saturated fat
- Trans fat
- Cholesterol
- Sodium
- Total carbohydrates
- Fiber
- Sugars
- Protein
In addition, calorie information must be declared on signs adjacent to foods on display and self-serve foods that are standard menu items. Covered establishments must have a reasonable basis to determine the nutrient information for standard menu items, including nutrient databases, lab analysis, Nutrition Facts labels, cookbooks, and other reasonable means.
⇒ Requirements for Succinct Statement
- It must be displayed at the bottom of each page of the menu and on the bottom of the menu board, positioned near the statement about additional nutrition information.
- The font size should match or exceed the smallest font used for calorie declarations on the same menu or board, with specific color and contrast requirements.
- Optional alternate statements are available for children’s menus and boards.
Caloric content for each standard menu item must be listed:
- Adjacent to the item name or price.
- In a font size no smaller than that of the item name or price, whichever is smaller.
- In a color as conspicuous as or more so than the item name, with similar background contrast or a background at least as contrasting as that used for the name of the associated standard menu item.
⇒ Documentation Requirements Needed
Upon request, restaurants or comparable retail food outlets are required to furnish the FDA with specific documentation within a reasonable timeframe, typically 4-6 weeks, entailing:
- Evidence supporting the nutrient content, along with details regarding the methodology and data utilized in determining these values.
- Confirmation that the establishment has implemented appropriate measures to ensure that the preparation method and portion sizes of standard menu items align with the criteria used to establish their nutrient values.
- Verification of employee training in maintaining consistent procedures and protocols for recipe development and restaurant operations.
Looking Forward
Moving forward, restaurants should contemplate several key aspects: Firstly, designating a responsible individual for the continuous task of menu labeling is imperative. Secondly, establishing a clear procedure for updating menu items, especially with new additions or alterations in ingredients, is crucial to ascertaining the accuracy of nutritional information displayed on menus, boards, or placards. Thirdly, devising effective communication strategies to relay this information both to employees and customers is essential. Lastly, continuing ongoing training programs for existing and incoming staff members ensures adherence to established procedures over time.
Smart Food Safe as a Digital Instrument in Adhering to Menu Labeling Requirements
Food establishments can optimize their menu labeling compliance process with Smart Food Safe’s multi-functional suite of software modules by integrating with their operations to enable precise and real-time tracking and analysis of nutritional information, allergens, and ingredients across menus.
Smart Food Safe offers comprehensive support in complying with menu labeling requirements by facilitating various key aspects:
Firstly, it simplifies the process of gathering nutritional information for menu items, providing a centralized platform for restaurants with Smart Supplier to input and manage data from suppliers for ingredients that make up the menu, Smart Specification to streamline specification requirements, Smart Lab to manage laboratory analysis process essential when dealing with complex menu items, and Smart Compliance for the automated verification of the specifications. Secondly, Smart Training aids in staff training by offering an effective online learning management system to ensure that employees are well-informed and equipped to adhere to regulations. Finally, Smart Docs systematizes the documentation and regulatory overview process for food businesses to stay up-to-date with menu labeling compliance standards.

 French
French
 Spanish
Spanish
 Portuguese
Portuguese
